As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Should You Juice?
Should You Juice? One glass of carrot juice might seem like the elixir of health to some, yet surprisingly, it requires about four medium carrots to produce. This leads us to ponder: is juicing really the most effective way to consume nutrients? With this nutrient-dense concentrate so popular, it’s crucial to understand the actual benefits and pitfalls of this practice.
No products found.
Historically, juicing has been lauded for its potential to deliver quick vitamins and minerals. However, a significant statistic to consider is that juicing can strip away essential fiber, which plays a vital role in digestion. Combining the ancient practice of juicing with modern knowledge, it’s crucial to strike a balance that ensures nutrient retention and health benefits.
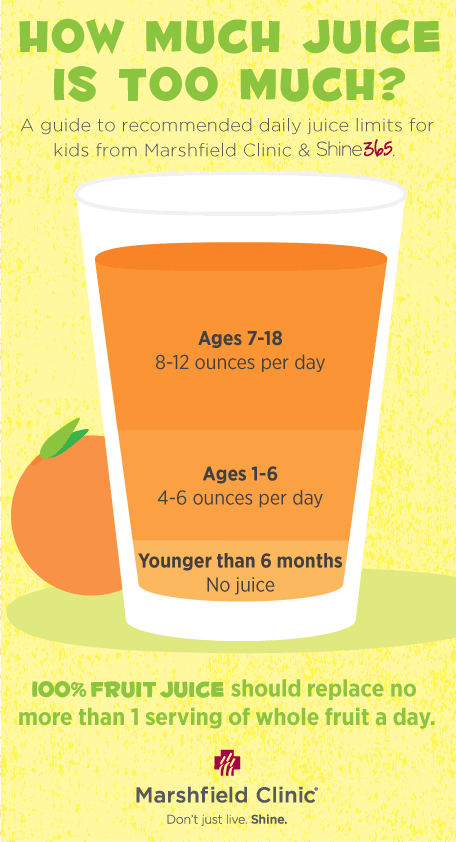
Exploring the concept of Juicing
Juicing is the process of extracting liquid from fruits and vegetables. This liquid, rich in vitamins and minerals, can be a refreshing beverage. While juicing removes some fiber, it concentrates nutrients. People often drink juice for a quick nutritional boost. However, it is essential to know its benefits and drawbacks.
The popularity of juicing has surged in recent years. Many believe it’s a convenient way to increase fruit and vegetable intake. Freshly made juice can be more nutritious than store-bought versions because it doesn’t contain added sugars or preservatives. Popular juicing ingredients include carrots, kale, and apples. These ingredients offer various health benefits and flavors.
With the rise of juicing, several types of juicers are available. They include centrifugal, masticating, and triturating juicers. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages. Centrifugal juicers are fast but may produce heat that destroys some nutrients. Masticating juicers work slowly but retain more nutrients and fiber.
Juicing can be part of a balanced diet if done correctly. Combining juice with whole fruits and vegetables ensures adequate fiber intake. Also, it’s crucial not to rely solely on juices for nutrition. Pairing juices with protein or healthy fats can enhance absorption. Always research and consult professionals to make informed choices.
History and Evolution of Juicing
The practice of juicing dates back to ancient times. Cultures like the Egyptians and Greeks enjoyed fresh juices for both nutrition and medicinal purposes.This early form of juicing often involved manually crushing fruits and vegetables. Over time, these methods evolved, leading to more advanced techniques. The essence remained the same: extracting beneficial nutrients in liquid form.
In the 20th century, the invention of the mechanical juicer changed the game. These devices made it easier for people to extract juice at home. With the rise of health movements in the 1970s, juicing gained significant popularity. People began to view it as an efficient way to consume more vitamins and minerals. This trend has only grown in recent decades.
The 1990s brought a surge of commercial juice bars. Places like Jamba Juice and Juice It Up! became household names. These establishments made fresh juice more accessible to the public. Customers flocked to these venues for their daily dose of fresh nutrients. As a result, the juicing industry saw considerable growth.
Today, juicing is a global phenomenon with a diverse following. Modern juicers are more efficient, extracting maximum nutrients and minimizing waste. Specialty juice stores and home juicing have evolved the market even further. Technological advancements allow for preservation techniques that maintain the juice’s nutritional value. This evolution shows the enduring appeal of juicing across generations.
Benefits of Juicing for Health
Juicing can significantly boost one’s intake of essential vitamins and minerals. A glass of freshly squeezed juice provides a concentrated dose of nutrients from fruits and vegetables. This can be especially helpful for those who struggle to eat enough produce daily. Drinking juice can make it easier to incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into the diet. Additionally, it provides an immediate source of energy.
Another advantage of juicing is hydration. Many fruits and vegetables have high water content, contributing to fluid intake. Staying hydrated helps maintain skin health, supports digestion, and boosts overall energy levels. By drinking juice, you not only consume essential nutrients but also keep your body hydrated. This is particularly beneficial during hot weather or vigorous activities.
Juicing also aids in digestion and detoxification. Fresh juices contain enzymes that can assist in breaking down food and improving nutrient absorption. These enzymes promote a healthier digestive system. Additionally, certain ingredients like ginger and lemon help cleanse the liver and flush out toxins. This makes juicing a popular choice for those looking to detoxify their bodies.
Including juice in your diet can support the immune system. Many fruits and vegetables like oranges, carrots, and spinach are rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants fight off free radicals and reduce inflammation, aiding in disease prevention. Regularly consuming fresh juice can strengthen your immune defenses. This makes it easier to ward off illnesses.
Drawbacks of Juicing
One notable drawback of juicing is the removal of fiber. Fiber is essential for digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. When fruits and vegetables are juiced, their fiber content is largely lost. This can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar, especially if the juice contains high-sugar fruits. Over time, these spikes can cause more health issues.
Additionally, juicing can be quite expensive. Fresh fruits and vegetables, especially organic ones, can cost a lot. When juicing regularly, the cost adds up quickly. Furthermore, high-quality juicers can be pricey, and not everyone can afford one. This makes maintaining a juicing habit financially challenging for some.
Juicing often results in consuming more calories than intended. When drinking juice, it’s easy to overlook the number of calories being consumed. A large glass of juice can contain several servings of fruit, leading to higher caloric intake. Consuming too many calories can contribute to weight gain. Moderation is key to avoiding this pitfall.
Another issue is the potential for nutrient imbalances. Relying solely on juice can lead to missing out on essential nutrients found in other foods. While juice provides vitamins and minerals, it lacks protein and healthy fats. These are crucial for a balanced diet. Ensuring a varied intake of different food types is important.
Lastly, juices can spoil quickly. Freshly made juice has a short shelf life, often just a few days. This requires consuming the juice soon after it’s made, which might not always be convenient. Additionally, improper storage can lead to bacterial growth. Ensuring proper storage practices is necessary to avoid health risks.
Alternative Ways to Consume Fruits and Vegetables
Smoothies are a popular and nutritious alternative to juicing. Unlike juices, smoothies retain the fiber from the fruits and vegetables. This makes them more filling and beneficial for digestion. Smoothies can be easily customized by adding yogurt, nuts, or seeds. This provides a balanced mix of protein and healthy fats.
Salads offer another excellent way to consume a variety of fruits and vegetables. They can include greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, and other colorful produce. Adding lean proteins like chicken or tofu enhances their nutritional value. Salads are easy to prepare and can be dressed with healthy oils or vinaigrettes. Incorporating different textures and flavors keeps salads exciting.
Cooking vegetables can enhance their flavors and make them more palatable. Steaming, roasting, and sautéing are great methods to keep nutrients intact. Adding spices and herbs can elevate the taste, making vegetables more enjoyable to eat. Cooking in batches allows for meal planning, saving time during busy weeks. It also ensures a steady intake of essential nutrients.
Snacks like veggie sticks with hummus are convenient and healthy. They require minimal preparation and can be easily packed for on-the-go consumption. Hummus, made from chickpeas, provides protein and healthy fats. Pairing it with carrots, celery, and bell peppers creates a tasty and nutritious snack. This encourages consistent fruit and vegetable intake throughout the day.
Incorporating fruits and vegetables into main dishes is also effective. Soups, stir-fries, and casseroles can contain a variety of produce. These dishes make it easy to eat a balanced diet. Experimenting with different recipes ensures variety and keeps meals interesting. This approach seamlessly integrates more nutrients into everyday dining.
Expert Opinions on Juicing
Nutritionists often emphasize the pros and cons of juicing. Many experts agree that juicing provides a convenient way to consume a variety of nutrients. However, they also caution about the lack of fiber. Registered dietitian, Sarah Schlichter, states, “While juice can be a good supplement, it should not replace whole fruits and vegetables.” Balance and moderation are key.
Some health professionals point out the high sugar content in fruit juices. Dr. Amy Lee, a bariatric physician, mentions that consuming too much fruit juice can spike blood sugar levels. This can be problematic for those with diabetes or blood sugar issues. She suggests incorporating more vegetables into juices to lower sugar content. Mixing in greens like kale or spinach can be beneficial.
Fitness experts also weigh in on the topic. Personal trainer, John Smith, highlights that juicing can be a great post-workout option. It helps in quick nutrient absorption and hydration. However, he advises pairing juice with a protein source. This ensures that muscles receive the necessary nutrients for recovery.
On the other hand, some experts question the long-term health benefits of juicing. Dr. Jane Doe, a nutrition researcher, argues that relying heavily on juice might lead to nutritional imbalances. She notes that a diet lacking in sufficient fiber and protein can be detrimental. She recommends a holistic approach, combining juice with balanced meals. This ensures sustained health benefits over time.
Holistic health practitioners also offer insight. They advise mindful consumption, emphasizing the importance of fresh, organic produce. “Quality matters as much as quantity,” says holistic nutritionist Emma Brown. She recommends rotating different fruits and vegetables to maximize nutrient diversity. This approach helps maintain a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Juicing is popular for its perceived health benefits. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand more about this practice.
1. What are the main benefits of juicing?
Juicing provides a concentrated dose of vitamins and minerals, making it easier to consume large amounts of nutrients quickly. It can also be a convenient way to include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet, especially for those who may not enjoy eating them whole.
Additionally, juicing can increase hydration since many fruits and vegetables have high water content. This helps support skin health, digestion, and overall energy levels. Drinking fresh juice regularly can complement a balanced diet though it’s important not to rely solely on juices for nutrition.
2. Are there any risks associated with juicing?
One key risk is the potential for elevated sugar levels, especially when using fruits with high sugar content like apples or grapes. Consuming high-sugar juices can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar, which might be problematic for individuals with diabetes or other related conditions.
Another concern is the removal of fiber from fruits and vegetables during the juicing process. Fiber is essential for digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Without it, you might miss out on these valuable benefits.
3. How does juicing compare to blending?
Juicing extracts liquid from fruits and vegetables while removing pulp and fiber which results in a smoother texture but less dietary fiber intake. Blending includes all parts of the produce like skins and seeds which provide more fiber but result in thicker consistency drinks like smoothies.
This means that blending maintains more nutrients that promote fullness and aid digestion due to higher fiber content whereas juicing offers quick nutrient absorption without the bulkiness of fibers. Choosing between them depends on your nutritional goals.
4. What types of vegetables are best for juicing?
Packed with vitamins and minerals leafy greens such as kale, spinach, or Swiss chard work exceptionally well in juices because they deliver lots of nutrients without contributing excessive sugar content furthermore; cucumbers or celery add hydration elements along with mild flavors making them versatile options too!
Add-ons like carrots bring sweetness while being rich sources beta-carotene great eyesight & immune system also beets provide antioxidants enhancing exercise performance adding varied colorful veggies into mix ensures diverse range beneficial compounds.
5.How often should one juice?
The frequency depends on individual health objectives consuming fresh juice daily doable supplement balanced diet however strictly exclusive fruit/vegetable diet unsustainable long term lacking proteins healthy fats consider starting once or twice week observe body responses adjust accordingly incorporating moderation pivotal avoiding nutritional gaps balancing whole foods varieties crucial maintaining overall wellness balanced regimes advisable seek professional nutritionist guidance ensure optimal personalized approaches adhering recommendation limits infeasible practices.
*Consider seeking professional nutritionist guidance personalized approaches.*
Conclusion
Juicing can be a beneficial addition to your diet, providing a concentrated source of essential nutrients. However, it’s important to balance juicing with whole fruits and vegetables to ensure fiber intake. Moderation and variety are key to reaping the full health benefits.
Experts recommend incorporating juicing as part of a broader, balanced nutritional strategy. Consulting with a healthcare professional can tailor the approach to individual health needs. Ultimately, juicing should complement a well-rounded diet for optimal health.

Maksuda Khanam is a passionate home appliance expert and the primary author behind KitchenMarts.com






