As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Do Microwave Ovens Emit Radiation?
Do Microwave Ovens Emit Radiation? In a world of rapid technological advancements, the safety of everyday appliances often comes into question. Consider the microwave oven, a staple in most modern kitchens. Are we exposing ourselves to harmful radiation every time we heat up leftovers?
Microwave ovens do emit radiation, but it’s non-ionizing and therefore not harmful. Invented in the 1940s, these appliances use microwave radiation to agitate water molecules, producing heat. The FDA regulates microwave ovens, ensuring safety through stringent standards and numerous research studies have shown them to be safe when used correctly.
Do Microwave Ovens Emit Radiation?
Microwave ovens use a type of electromagnetic radiation called microwaves to cook food. This radiation is non-ionizing, meaning it doesn’t have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms or molecules. It’s different from ionizing radiation found in X-rays, which can be harmful. When you turn on a microwave, it sends microwaves to the food, causing water molecules to move and create heat. This process heats the food quickly and efficiently.
Some people worry that microwave ovens might leak radiation. However, modern microwaves are designed with safety features to prevent this. The doors of microwave ovens have a special mesh that keeps the microwaves inside. Additionally, most microwaves stop producing radiation as soon as you open the door. This ensures that the radiation is contained and not harmful to users.
The FDA has strict regulations for microwave ovens to keep them safe. Manufacturers must test each unit to ensure it meets these standards. They also conduct periodic inspections to ensure compliance. If a microwave doesn’t meet the safety requirements, it cannot be sold. This strict oversight helps protect consumers from any potential dangers of radiation leakage.
To use your microwave safely, follow some simple guidelines. Always make sure the door seals properly and isn’t damaged. Avoid running the microwave when it’s empty, as this can cause overheating. Stay at least an arm’s length away from the microwave while it’s operating. By following these tips, you can enjoy the convenience of microwave cooking without worrying about radiation.
The Science Behind Microwave Ovens and Radiation
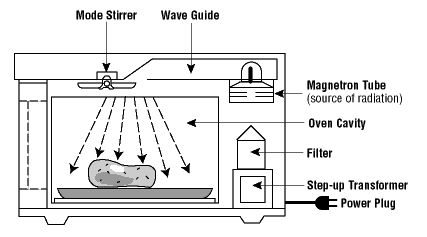
Microwave ovens work by emitting microwaves, a type of electromagnetic radiation. These waves are absorbed by water, fats, and sugars in food, causing the molecules to vibrate. This vibration produces heat, which cooks the food. The microwave oven is able to do this because it uses a component called a magnetron to produce microwaves. The magnetron converts electrical energy into microwave radiation that heats the food efficiently and uniformly.
Unlike ionizing radiation like X-rays, microwave radiation is non-ionizing. Non-ionizing radiation doesn’t have enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms or molecules. Instead, it only makes them vibrate, which is why it’s safe for cooking. This safety aspect has been rigorously tested, ensuring that microwave ovens do not pose health risks when used correctly. Manufacturers follow strict guidelines to ensure the levels of emitted radiation are well within safety limits.
Microwaves are uniquely suited for heating food because they can penetrate up to an inch into the food. This is different from conventional ovens, which cook from the outside in. The ability to penetrate and heat food quickly makes microwaves a time-efficient way to cook. The rotating turntable in most microwaves ensures even cooking by rotating the dish, allowing microwaves to hit all parts of the food equally. This method helps avoid cold spots and ensures thorough heating.
Safety features in modern microwaves are crucial. These devices have built-in mechanisms to prevent the emission of microwaves when the door is open.
- Special mesh screens are integrated into the door to block microwaves from escaping.
- Interlocking switches ensure the microwave stops when the door is opened.
- Heat sensors automatically turn off the microwave if it overheats.
Such safety measures are designed to protect users from any accidental exposure to microwaves, making them extremely reliable household appliances.
Types of Radiation: Ionizing vs Non-Ionizing
Radiation can be categorized into two main types: ionizing and non-ionizing. Ionizing radiation has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, creating ions. This process can cause significant damage to living tissue, leading to health risks like cancer. Common sources include X-rays, gamma rays, and some ultraviolet (UV) light. Due to these risks, ionizing radiation is used with great caution and strict guidelines.
On the other hand, non-ionizing radiation doesn’t have the energy to ionize atoms. Instead, it only makes molecules vibrate or move. This type includes microwaves, radio waves, and visible light. Non-ionizing radiation is generally considered safe for everyday use. For example, microwaves use non-ionizing radiation to heat food without altering its molecular structure.
Understanding the differences is essential for safely using various technologies. Ionizing radiation is used in medical imaging and cancer treatments, making it highly valuable despite its risks. Non-ionizing radiation is widespread in daily life, from cell phones to WiFi networks. The key is using each type within its safe limits to avoid any potential harm.
Here’s a quick comparison of ionizing vs. non-ionizing radiation:
| Type | Energy Level | Examples | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionizing | High | X-rays, Gamma rays, UV light | Medical imaging, Cancer treatment |
| Non-Ionizing | Low | Microwaves, Radio waves, Visible light | Cooking, Communication, Lighting |
Understanding these details can help you make informed decisions about the technology you use every day.
Safety Measures in Design: How Microwaves Prevent Radiation Leakage
Modern microwave ovens incorporate several safety features to prevent radiation leakage. One of the primary measures is the use of a metal mesh on the oven door. This mesh has tiny holes that block microwaves from escaping while allowing you to see inside. The mesh works on the principle that microwaves, which have a longer wavelength, cannot pass through the small holes. This design ensures that radiation stays within the oven.
Another crucial safety feature is the interlock system. Microwaves are equipped with multiple interlocking switches connected to the door. These switches ensure that the microwave stops generating radiation as soon as the door is opened. Even if one switch fails, the others will still prevent the microwave from operating. This redundancy adds an extra layer of safety.
The materials used in constructing microwave ovens also play a significant role in safety. The interior of most microwaves is lined with metal, which reflects microwaves, keeping them confined to the oven’s cavity. This reflective quality ensures that the microwaves target your food, cooking it evenly without escaping. The outer casing, usually made of sturdy plastic or metal, also helps contain any residual radiation.
Regular maintenance and proper usage are also essential for safety. Users should regularly inspect the door seals and hinges to ensure they are in good condition. Damaged seals can allow microwaves to leak, posing a risk. It’s also important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions, such as not using metal objects inside the microwave, to avoid any malfunction. Proper maintenance ensures that safety features continue to function correctly.
Here are some common safety guidelines for microwave use:
- Avoid using the microwave if the door doesn’t seal properly.
- Do not operate the microwave when it’s empty, as this can damage the magnetron.
- Use only microwave-safe containers to avoid harmful chemical leaching.
- Ensure the interior is clean to avoid any issues with reflective surfaces.
Following these guidelines helps maintain the integrity of the microwave and its safety features.
FDA Regulations for Microwave Ovens
The FDA, or Food and Drug Administration, sets strict regulations for the safety of microwave ovens. These regulations ensure that microwave ovens produced and sold in the United States meet safety standards. The FDA conducts thorough inspections of microwave ovens before they are released to the market. Manufacturers are required to test each unit for radiation leakage. Any microwave that does not meet these stringent guidelines cannot be sold.
One key regulation focuses on limiting the amount of radiation leakage. The FDA mandates that microwave ovens must not emit more than 5 milliwatts of radiation per square centimeter at approximately 2 inches from the oven surface. This limit ensures that even if there is a small amount of leakage, it will not be harmful to human health. The FDA continuously reviews scientific research to update these regulations as needed. This helps keep the standards up-to-date with the latest safety information.
Microwave manufacturers must also include safety features to prevent microwaves from operating when doors are open. These safety features ensure that no radiation is emitted when the door is ajar. The FDA inspects these features to verify that they are functioning correctly. Additionally, the FDA requires clear labeling on microwave ovens to inform consumers about their safe use. Instructions on avoiding metal objects and ensuring door seals are in good condition are part of these labels.
Consumers have a role in adhering to FDA guidelines by using microwaves properly. Following the manufacturer’s instructions is essential for maintaining safety. Regularly checking the door seals and hinges can help prevent potential radiation leakage. Proper use and maintenance extend the lifespan of the microwave while keeping the user safe. Knowing these FDA regulations can give users peace of mind when using their microwave ovens.
The FDA also enforces labeling regulations:
- Instructions on safe usage and maintenance.
- Warnings about potential hazards, such as using metal objects.
- Labels explaining the importance of door seal integrity.
- Information on avoiding microwave misuse to prevent fires.
These labels help ensure that users are well-informed about how to safely operate their microwave ovens.
Proper Microwave Usage to Mitigate Risks
Following proper microwave usage guidelines can significantly mitigate risks and enhance safety. Start by ensuring that your microwave’s door seals are intact and not damaged. If you notice any issues with the seal, it’s essential to get it repaired or replaced. Avoid slamming the door as it can damage the seals over time. Keeping seals in good condition helps prevent radiation leakage, ensuring the microwave operates safely.
Always use microwave-safe containers when heating food. Some materials, like metal or some plastics, can cause fires or release harmful chemicals. Look for containers labeled as microwave-safe to avoid these dangers. Additionally, it’s beneficial to stir food halfway through the cooking process to ensure even heating. Uneven heating can lead to cold spots where bacteria may survive.
Avoid running the microwave when it’s empty. Without anything to absorb the microwaves, the energy will bounce around inside, possibly damaging the appliance’s components. This can lead to potential hazards over time. It’s also a good practice to maintain a few inches of space around the microwave to allow for proper ventilation. Overheating can be avoided by following this simple spacing rule.
Cleaning the microwave regularly also helps maintain its efficiency and safety. Food spills can cause uneven cooking and even flare-ups if left unattended. Use a damp cloth to wipe down the interior after each use. Make sure to clean the door seals and hinges as well. Ensuring the cleanliness of your microwave not only keeps it running smoothly but also extends its lifespan.
Here are some additional tips for safe microwave use:
- Do not use metal utensils or cookware in the microwave.
- Avoid microwaving sealed containers; they might explode due to pressure build-up.
- Use a microwave cover to prevent food splatters and ensure even cooking.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety instructions.
By adhering to these tips, you can minimize risks and ensure your microwave’s safe and efficient operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Microwave ovens are common household appliances, but many people have questions about their safety and functionality. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand more about microwaves.
1. How do microwave ovens heat food?
Microwave ovens heat food using a type of electromagnetic radiation called microwaves. These waves penetrate the food and cause water molecules to vibrate, generating heat. This process cooks the food quickly and evenly from the inside out. The energy is targeted specifically at water molecules, making it very efficient for heating moist foods.
The rotating plate in most microwave ovens helps distribute these waves more evenly across your meal. Without this feature, some parts of your food might remain cold while others get hot. Properly arranging food inside the microwave can ensure even cooking. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for best results.
2. Are there foods that shouldn’t be microwaved?
Yes, certain foods should not be microwaved due to potential safety risks or poor cooking results. Foods like eggs in their shells can explode because steam builds up inside without a way to escape. Grapes and hot peppers can also react poorly under microwave radiation, creating sparks or releasing harmful chemicals.
Additionally, avoid microwaving processed meats high in preservatives, as these chemicals can break down into potentially hazardous compounds when heated rapidly. Always check labels and use microwave-safe containers for best practices when preparing meals with your appliance.
3. Can microwaving damage nutrients in food?
Certain cooking methods can reduce the nutrient content of foods, but microwaving generally preserves nutrients better than other techniques like boiling or frying. Because microwaving cooks foods quickly with minimal water, essential vitamins and minerals are less likely to leach out or degrade under heat.
The key is not overcooking your dishes; excessive cooking time can still result in nutrient loss regardless of method used. It’s often recommended to use shorter cooking times at lower power settings whenever possible to keep more nutritional value intact in vegetables and fruits.
4. What should I do if my microwave has a broken door seal?
A faulty door seal on a microwave is a serious issue that needs immediate attention as it may allow radiation leakage which could be harmful over prolonged exposure periods If you notice any damage such as cracks tears etc on door seals discontinue its usage immediately until fixed professionally by qualified technician
You might also want consider replacing whole unit particularly if old model since newer models come equipped enhanced safety features higher energy efficiency ratings cost-effective long run Besides taking precautionary measures ensure safe proper functioning appliance paramount importance safeguard health well-being family members household
5. Is it safe to stand close to a working microwave oven?
Morden Microwave designs ensure minimal radiation exposure during operation through stringent safety standards including well-sealed doors proper materials construction Therefore standing near operating unit poses significant health risk However advisable maintain slight distance avoid directly peering through window while running prevent unnecessary strain eyes possible accidental burns hot surfaces appliance body exterior
If concerned about levels emissions reputable agency certified products easily accessible marketplace strict governance quality control measures adherence guidelines So rest assured practicing basic precaution upkeep optimal performance everyday domestic life convenience retained without compromise estrutouction risk factorschefchef chef chef chapion chahefchefd proaructive yield effiy< brCaster especially focusing young ones sensitive human bodies systems.p.babies kids toddlers require extra </P
Conclusion
Understanding the science and safety measures behind microwave ovens can help demystify their use in our daily lives. By following proper guidelines, we can enjoy the convenience they offer without worrying about harmful radiation. Remember, always use microwave-safe containers and regularly inspect your appliance for any damage.
Ongoing regulations and advancements ensure that microwave ovens remain safe household items. As technology evolves, these appliances will continue to become even safer and more efficient. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions and ensure the safety of your home and family.

Maksuda Khanam is a passionate home appliance expert and the primary author behind KitchenMarts.com






